
Activating function (AF, gradient of the electric field) of the
The gradient of the electric field is the second derivative of the electrostatic potential, and as such, it obeys certain symmetries; The EFG is a symmetric tensor with zero trace.

Electric field gradient squared distribution on the surfaces of both
In atomic, molecular, and solid-state physics, the electric field gradient ( EFG) measures the rate of change of the electric field at an atomic nucleus generated by the electronic charge distribution and the other nuclei.
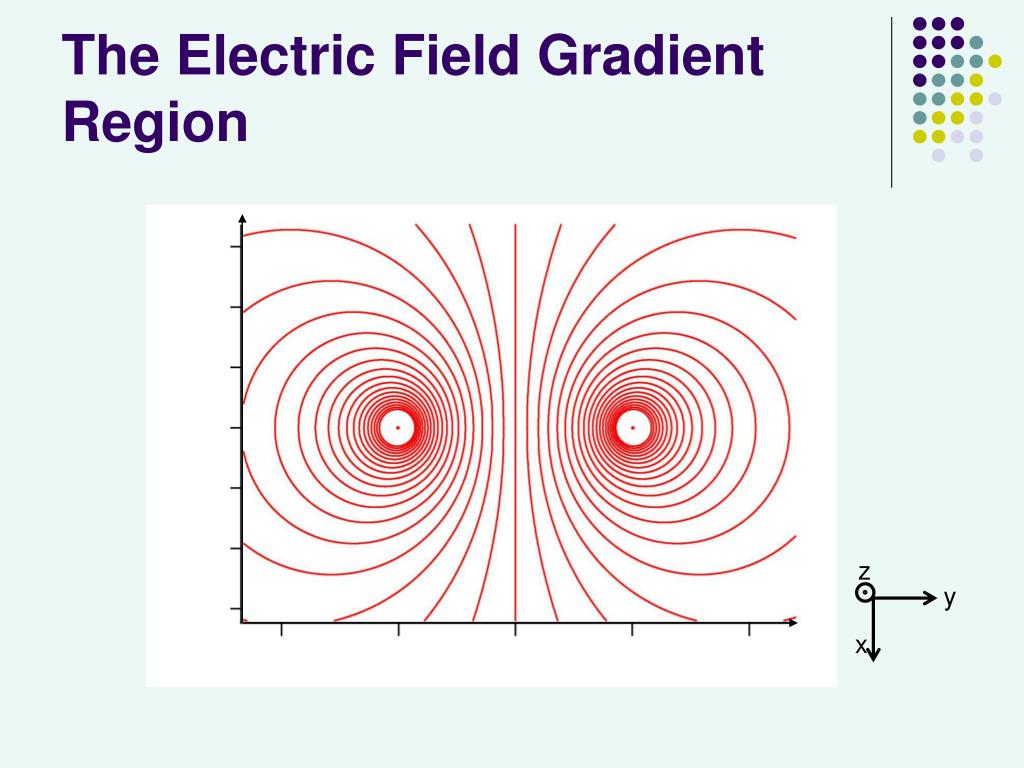
PPT Measuring Polarizability with an Atom Interferometer PowerPoint
The electric field is said to be the gradient (as in grade or slope) of the electric potential. For continually changing potentials, Δ V Δ V and Δ s Δ s become infinitesimals and differential calculus must be employed to determine the electric field.
a) Electric field gradient distribution at the tip region under DC bias
Droplet directional transport is one of the central topics in microfluidics and lab-on-a-chip applications. Selective transport of diverse droplets, particularly in another liquid phase environment with controlled directions, is still challenging. In this work, we propose an electric-field gradient-driven droplet directional transport platform facilitated by a robust lubricant surface. On the.
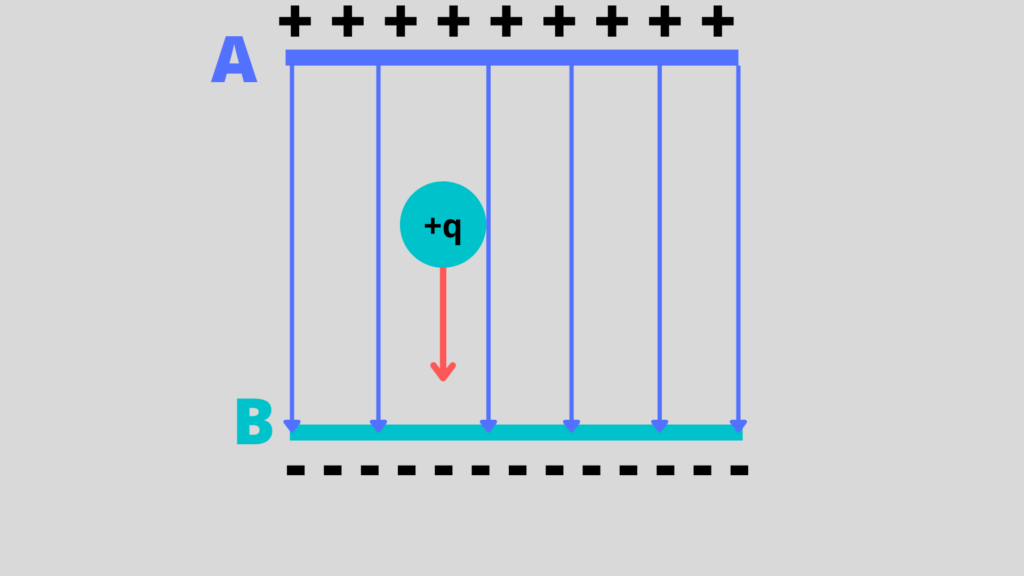
Electric Potential Electric Field as Potential Gradient
In vector calculus notation, the electric field is given by the negative of the gradient of the electric potential, E = − grad V. This expression specifies how the electric field is calculated at a given point. Since the field is a vector, it has both a direction and magnitude.

Contour plot of gradient of squared electric field strength, ∇E 2 rms
Measurement(s) electric field gradient Technology Type(s) computational modeling technique Factor Type(s) material studied Machine-accessible metadata file describing the reported data: https.
a) 2D plot of norm of electric field gradient b) Norm of electric field
5.14: Electric Field as the Gradient of Potential. where E(r) E ( r) is the electric field intensity at each point r r along C C. In Section 5.12, we defined the scalar electric potential field V(r) V ( r) as the electric potential difference at r r relative to a datum at infinity. In this section, we address the "inverse problem.

Electric field as potential gradient 12th physics SWAJ Foundation
Electric fields are caused by electric charges, described by Gauss's law, and time varying magnetic fields, described by Faraday's law of induction. Together, these laws are enough to define the behavior of the electric field. However. is the gradient of the electric potential and.

Relation Between Potential Gradient And Electric Field YouTube
7.14. With this notation, we can calculate the electric field from the potential with. E→ = −∇ V, E → = − ∇ → V, 7.15. a process we call calculating the gradient of the potential. If we have a system with either cylindrical or spherical symmetry, we only need to use the del operator in the appropriate coordinates: Cylindrical:∇.
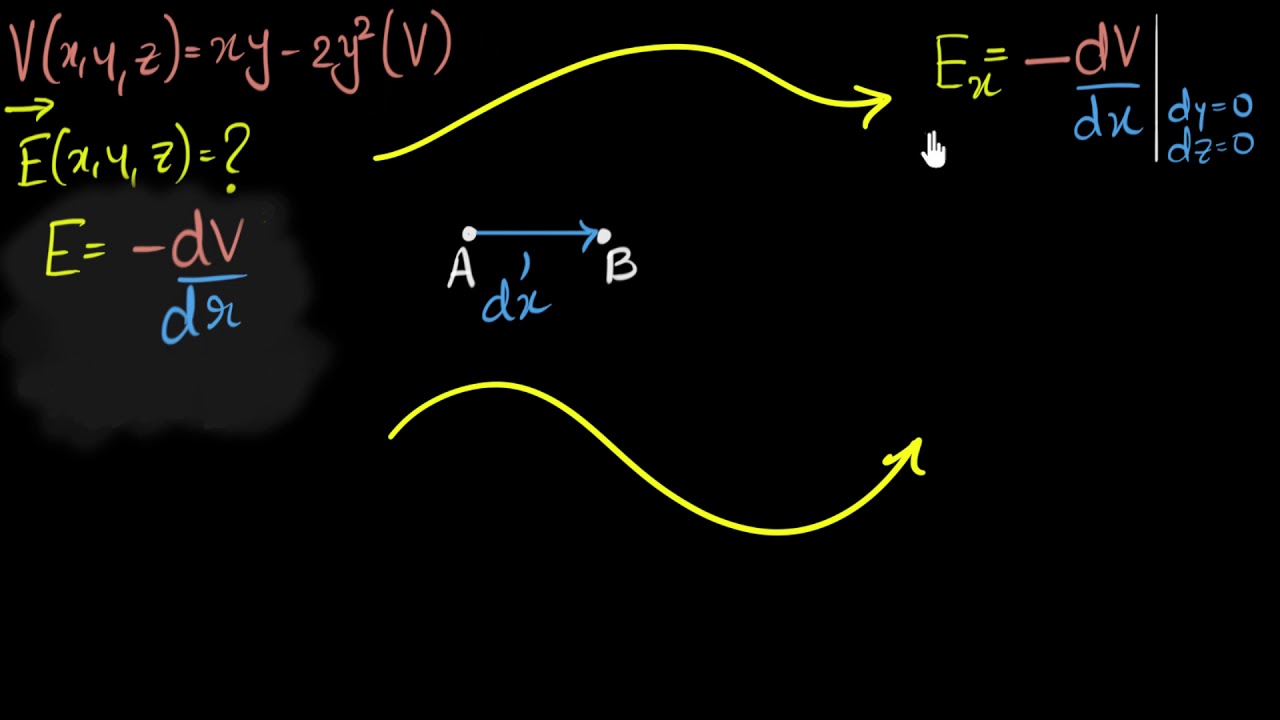
Calculating E from V(x,y,z) E = potential gradient Electrostatic
In physics, chemistry and biology, a potential gradient is the local rate of change of the potential with respect to displacement, i.e. spatial derivative, or gradient. This quantity frequently occurs in equations of physical processes because it leads to some form of flux . Definition One dimension

Finite element simulation with COMSOL; areas with different color
The gradient of a scalar field is a vector that points in the direction in which the field is most rapidly increasing, with the scalar part equal to the rate of change. A particularly important application of the gradient is that it relates the electric field intensity \({\bf E}({\bf r})\) to the electric potential field \(V({\bf r})\).
The gradient of electric field squared across the DEPwell C0 and the
Electric Field as the Gradient of Potential In Section 5.8, it was determined that the electrical potential difference measured over a path is given by (5.14.1) where is the electric field intensity at each point along . In Section 5.12, we defined the scalar electric potential field as the electric potential difference at

Lecture 4 Review of electrostatics pt. 2
The electric field doesn't depend on your choice for zero potential since the electric field is the gradient of the potential. Only differences in potential energy are meaningful, and electric potential is just electric potential per unit charge, so only differences in electric potential are meaningful. $\endgroup$ -

Electric Field as potential gradient Class 12 ElectrostaticsNCERT
The electric field is the gradient of the potential. The gradient is in the direction of the most rapid change of the potential, and is therefore perpendicular to an equipotential surface. If $\FLPE$ were not perpendicular to the surface, it would have a component in the surface. The potential would be changing in the surface, but then it.

Simulation of electric field gradient squared for cylindrical IDE
As shown in Figure 7.5.1, if we treat the distance Δs as very small so that the electric field is essentially constant over it, we find that. Es = − dV ds. Therefore, the electric field components in the Cartesian directions are given by. Ex = − ∂V ∂x, Ey = − ∂V ∂y, Ez = − ∂V ∂z. This allows us to define the "grad" or.
The simulation result of the electrical field and potential
A numerical model of oil-solid multi-gradient filtration with electric field enhancement was developed by coupling the electric field governing equation, flow field governing equations, discrete phase tracking equation, and particle-wall collision model equation.. When the electric field strength is 2 kV/mm, the inlet flow rate is 0.3 m.